Toward Computational Literature Review: Refining Expert-Built Dictionaries for Automated Analysis of Academic Texts
Abstract
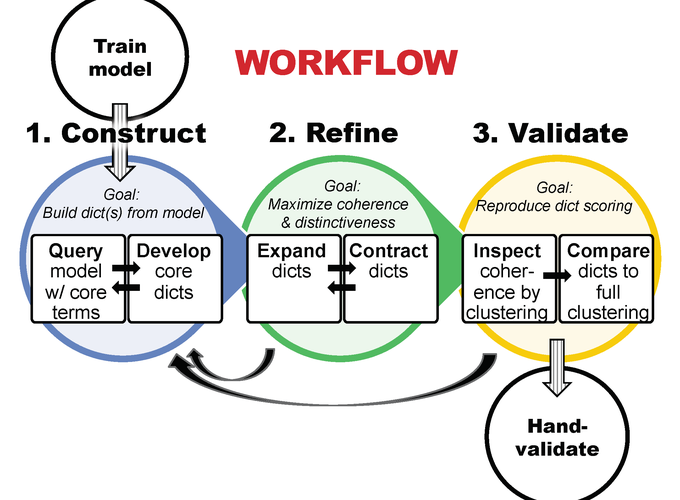
The social sciences face growing demand for reproducible tools for processing massive troves of often-complex text data (political speeches, medical notes, etc.). In response, we aim toward computational literature review by developing an inductive method of applying expert-built dictionaries for automated analysis of complex texts. Our workflow begins with developing dictionaries from foundational texts and domain expertise. Next, we apply text-analytic methods of differential domain-specificity and complexity to create vector-space representations of texts. Finally, we compare the validity of these methods by using regression models to evaluate relationships between their representations and ground truth. Taking as our use case a large corpus of academic articles in organizational science, we find that domain-specific, relatively simple embeddings were most valid–while the more sophisticated models were very weak. Thus, we suggest that social science workflows for learning from complex texts incorporate embeddings that are domain-specific and straightforward–rather than convoluted.